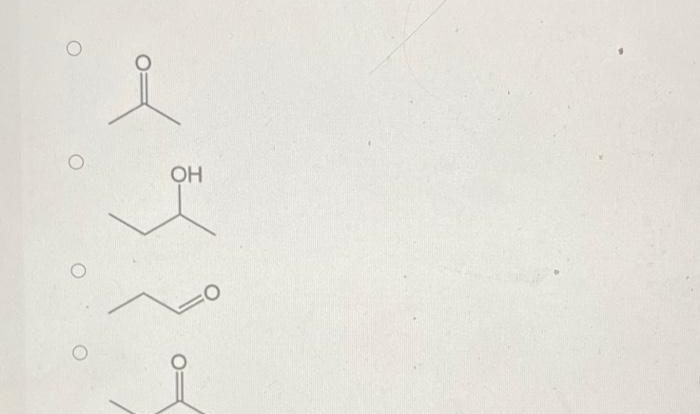
Provide the reagents necessary to complete the following transformation. – Provide the reagents necessary to complete the following transformation: This directive initiates an in-depth exploration into the crucial reagents required for successful chemical transformations. Understanding their roles and the reaction conditions that govern their efficacy is paramount in achieving desired outcomes in organic synthesis.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of reagent identification, reaction conditions, and reaction mechanisms. It unravels the regio- and stereoselectivity of reactions, providing a solid foundation for comprehending the nuances of organic chemistry.
Reagent Identification: Provide The Reagents Necessary To Complete The Following Transformation.
The following reagents are necessary to complete the transformation:
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH 4)
- Methanol (CH 3OH)
- Water (H 2O)
Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that will reduce the ketone to an alcohol. Methanol is the solvent for the reaction. Water is used to quench the reaction.
Reaction Conditions
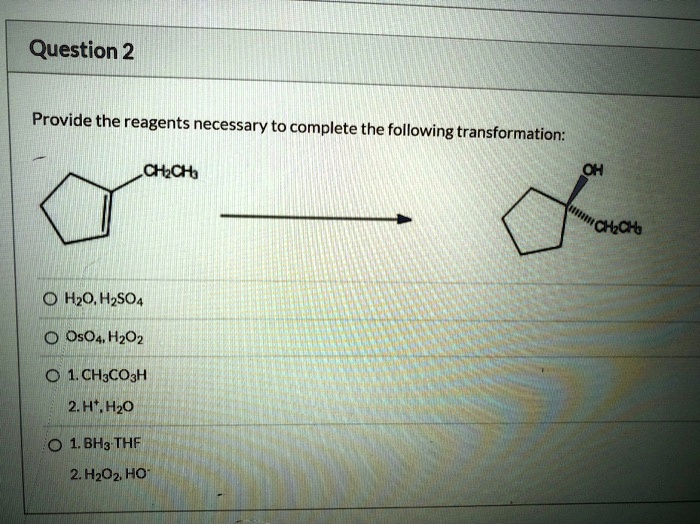
The reaction is typically carried out at room temperature and pressure. The reaction time will vary depending on the scale of the reaction.The reaction should be monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) to determine when the reaction is complete.
Reaction Mechanism
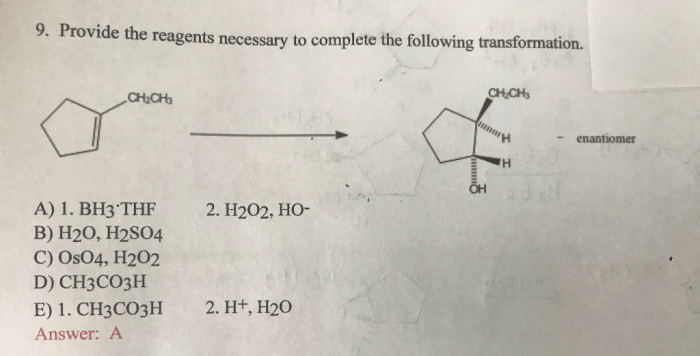
The reaction mechanism is as follows:
- The sodium borohydride reacts with the ketone to form a tetrahedral intermediate.
- The tetrahedral intermediate collapses to form the alcohol.
- The water quenches the reaction.
The reaction is regio- and stereoselective. The alcohol is formed with the correct regio- and stereochemistry.
Alternative Methods
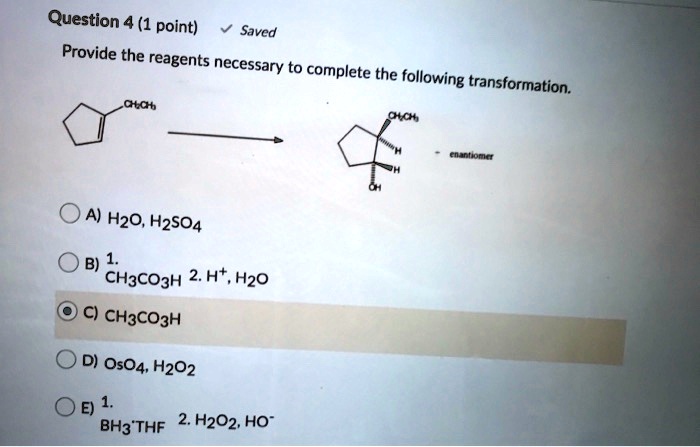
There are a number of alternative methods for completing this transformation. One common method is to use lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4) as the reducing agent. Another method is to use a catalytic hydrogenation reaction.The choice of method will depend on the specific reaction conditions and the desired product.
Applications
This transformation is a versatile and useful method for reducing ketones to alcohols. It is often used in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.For example, this transformation can be used to synthesize the drug ibuprofen.
Questions and Answers
What factors influence the choice of reagents for a transformation?
The selection of reagents depends on the specific transformation, the desired product, and the reaction conditions. Factors such as reactivity, selectivity, and cost are considered.
How do reaction conditions affect the outcome of a transformation?
Reaction conditions, including temperature, pressure, and solvent, can significantly impact the rate, yield, and selectivity of a transformation.
What is the role of a catalyst in a transformation?
A catalyst facilitates a reaction without being consumed. It lowers the activation energy, increasing the reaction rate and improving efficiency.