Fluid and electrolyte imbalance practice questions delve into the intricacies of fluid and electrolyte management, equipping healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to effectively assess, diagnose, and treat fluid and electrolyte imbalances. This comprehensive guide provides a deep understanding of the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for various fluid and electrolyte imbalances, empowering nurses and other healthcare providers to deliver optimal patient care.
Through a series of engaging case studies, interactive exercises, and in-depth discussions, this guide fosters a thorough understanding of the principles and practices of fluid and electrolyte management. By mastering the concepts presented in these practice questions, healthcare professionals can confidently navigate the complexities of fluid and electrolyte imbalances, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance Overview

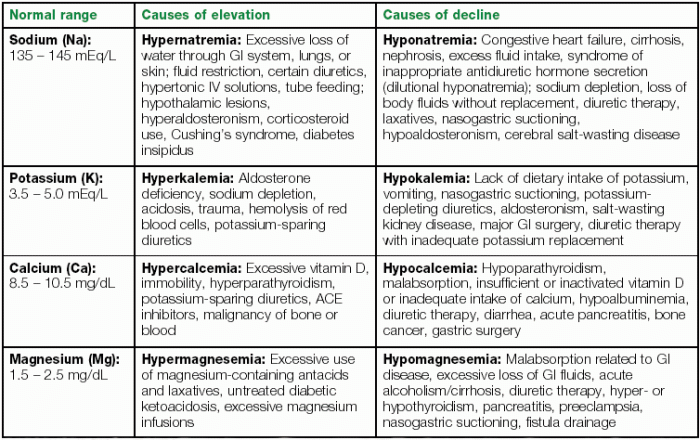
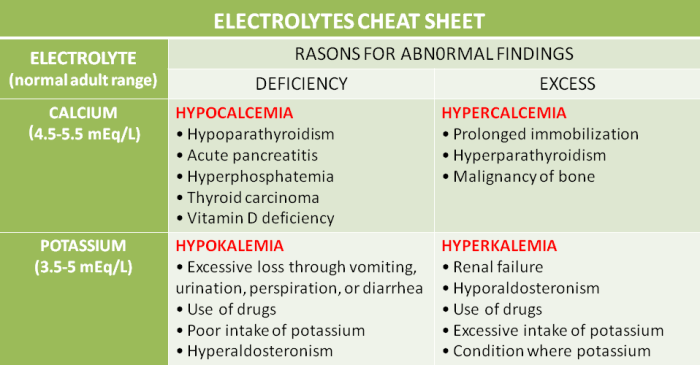
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances occur when the body’s fluid or electrolyte levels are abnormally high or low. These imbalances can lead to a variety of symptoms, including dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, and organ dysfunction.
There are three main types of fluid and electrolyte imbalances: hypervolemia, hypovolemia, and electrolyte imbalance.
- Hypervolemiais a condition in which there is too much fluid in the body. This can be caused by a number of factors, including heart failure, kidney failure, and liver disease.
- Hypovolemiais a condition in which there is not enough fluid in the body. This can be caused by a number of factors, including dehydration, bleeding, and diarrhea.
- Electrolyte imbalanceis a condition in which the levels of electrolytes in the body are abnormal. This can be caused by a number of factors, including dehydration, kidney disease, and certain medications.
Assessment and Diagnosis, Fluid and electrolyte imbalance practice questions
Assessing fluid and electrolyte imbalances involves a combination of physical examination, laboratory testing, and patient history.
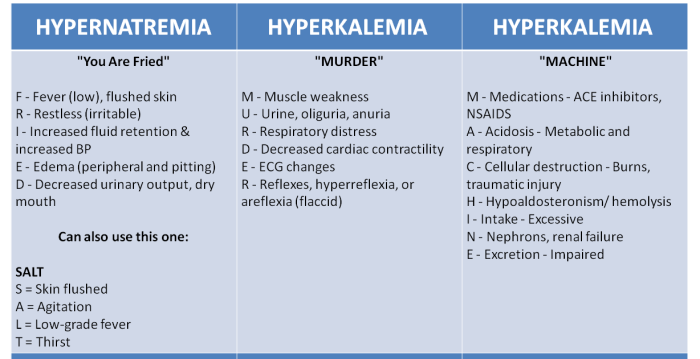
- Physical examinationcan reveal signs of dehydration, such as dry skin, sunken eyes, and decreased skin turgor. It can also reveal signs of electrolyte imbalance, such as muscle weakness, confusion, and arrhythmias.
- Laboratory testingcan measure the levels of electrolytes in the blood and urine. This can help to identify the type of fluid and electrolyte imbalance that is present.
- Patient historycan provide information about the patient’s symptoms, risk factors, and possible causes of the fluid and electrolyte imbalance.
Management and Treatment
The management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances depends on the type of imbalance that is present.
- Hypervolemiais treated by removing excess fluid from the body. This can be done through diuretics, fluid restriction, or dialysis.
- Hypovolemiais treated by replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. This can be done through intravenous fluids, oral fluids, or blood transfusions.
- Electrolyte imbalanceis treated by correcting the levels of electrolytes in the body. This can be done through intravenous fluids, oral supplements, or medications.
Nursing Interventions
Nurses play a vital role in monitoring and managing fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Monitor vital signsand fluid balance.
- Assess for signs and symptomsof fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
- Administer fluids and electrolytesas prescribed.
- Educate patientsabout fluid and electrolyte imbalances and their prevention.
Quick FAQs: Fluid And Electrolyte Imbalance Practice Questions
What are the common causes of fluid and electrolyte imbalances?
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances can result from various factors, including excessive fluid loss (e.g., vomiting, diarrhea), inadequate fluid intake, electrolyte imbalances (e.g., sodium, potassium), and underlying medical conditions (e.g., kidney disease, diabetes).
How do you assess for fluid and electrolyte imbalances?
Assessment involves a thorough patient history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Signs and symptoms may include changes in weight, skin turgor, vital signs, and electrolyte levels.
What are the principles of fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy?
Replacement therapy aims to restore fluid volume and electrolyte balance. Fluids and electrolytes are administered intravenously or orally, depending on the severity of the imbalance and the patient’s condition.