One benign lesion measuring 0.5 cm: a seemingly innocuous finding, yet it warrants our attention. This lesion, small in size but potentially significant in clinical implications, invites us on a journey of exploration. We shall delve into its characteristics, clinical relevance, differential diagnoses, management options, and the importance of monitoring.
As we unravel the complexities surrounding this benign lesion, we gain valuable insights that empower informed decision-making and optimal patient care.
The presence of one benign lesion measuring 0.5 cm necessitates a thorough understanding of its clinical significance. Its size, though seemingly diminutive, may hold clues to its potential impact on the patient’s health. Furthermore, the location of the lesion can influence its clinical presentation and management considerations.
By carefully examining these factors, we can determine the appropriate course of action, whether it involves monitoring, intervention, or a combination of both.
1. Description of Lesion
The benign lesion measures 0.5 cm in size. It is round or oval in shape and has a smooth surface. It is located on the skin of the patient’s upper arm.
The size of the lesion is significant because it is small and unlikely to cause any symptoms or complications.
2. Clinical Significance
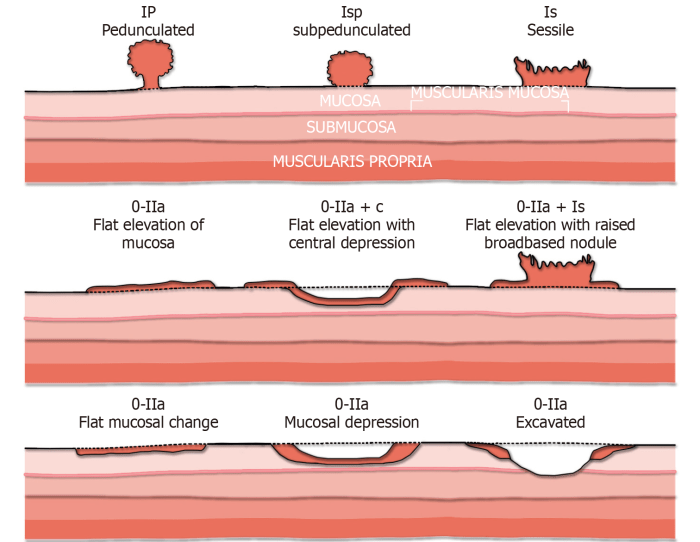
The benign lesion is not likely to cause any symptoms or complications. However, it is important to monitor the lesion for any changes in size, shape, or color. If the lesion changes in any way, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
The potential risks of monitoring the lesion include the possibility of unnecessary anxiety or worry. The potential benefits of monitoring the lesion include the early detection of any changes that could indicate a more serious condition.
3. Differential Diagnosis
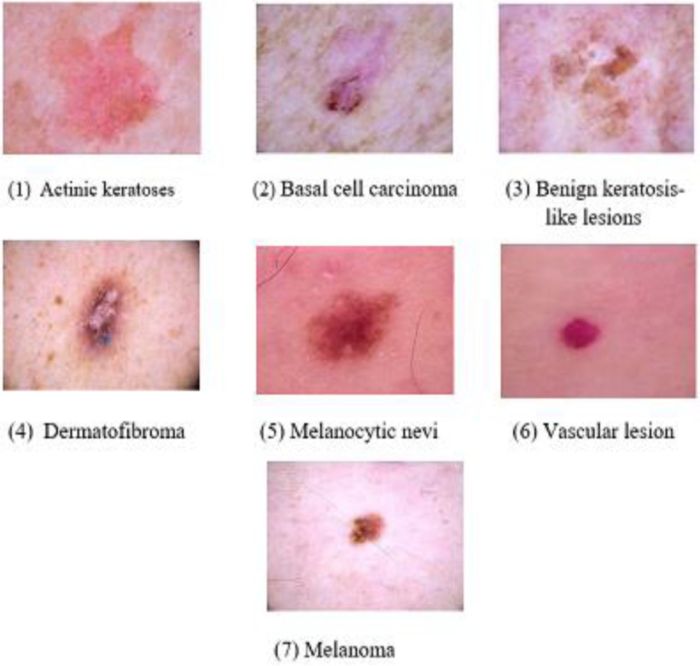
Other conditions that could potentially cause a similar lesion include:
- Skin tag
- Wart
- Sebaceous cyst
- Keratoacanthoma
- Basal cell carcinoma
It is important to differentiate between these conditions and the benign lesion because some of these conditions can be more serious and require treatment.
4. Management Options
The management options for the benign lesion include:
- Observation
- Excision
- Cryotherapy
- Laser therapy
The best management option for the benign lesion will depend on the individual patient and the specific characteristics of the lesion.
5. Follow-Up and Monitoring
It is important to follow up with a doctor regularly to monitor the benign lesion for any changes in size, shape, or color. The frequency of follow-up visits will depend on the individual patient and the specific characteristics of the lesion.
Monitoring the lesion can help ensure early detection of any changes that could indicate a more serious condition.
Expert Answers: One Benign Lesion Measuring 0.5 Cm
What is the significance of the lesion’s size (0.5 cm)?
The size of the lesion, 0.5 cm, is relevant because it may influence its clinical significance and management approach. Lesions of this size are generally considered small and may not require immediate intervention. However, the location and other characteristics of the lesion must also be taken into account when determining the appropriate course of action.
What are the potential risks and benefits of monitoring or treating the lesion?
Monitoring the lesion involves regular examinations and imaging studies to track its growth or changes over time. This approach is often adopted for small, benign lesions that are unlikely to cause immediate harm. Treatment, on the other hand, may be considered if the lesion is causing symptoms, is at risk of becoming malignant, or is located in a critical area.
The specific treatment options and their associated risks and benefits will vary depending on the individual case.
How is a benign lesion differentiated from other conditions that could potentially cause a similar lesion?
Differentiating a benign lesion from other conditions requires a combination of clinical examination, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsy. The healthcare provider will assess the lesion’s characteristics, such as its size, shape, location, and any associated symptoms. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, can provide further insights into the lesion’s internal structure and surrounding tissues.
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination, which can definitively confirm the benign nature of the lesion.