Delving into the AP Environmental Science Cheat Sheet, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence. The cheat sheet provides a concise yet comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles, concepts, and applications of environmental science, offering a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of this critical field.
As we delve deeper into the cheat sheet, we will explore the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the profound impact of human activities on the environment. We will examine the causes and effects of climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss, and discuss the importance of sustainable practices and environmental protection.
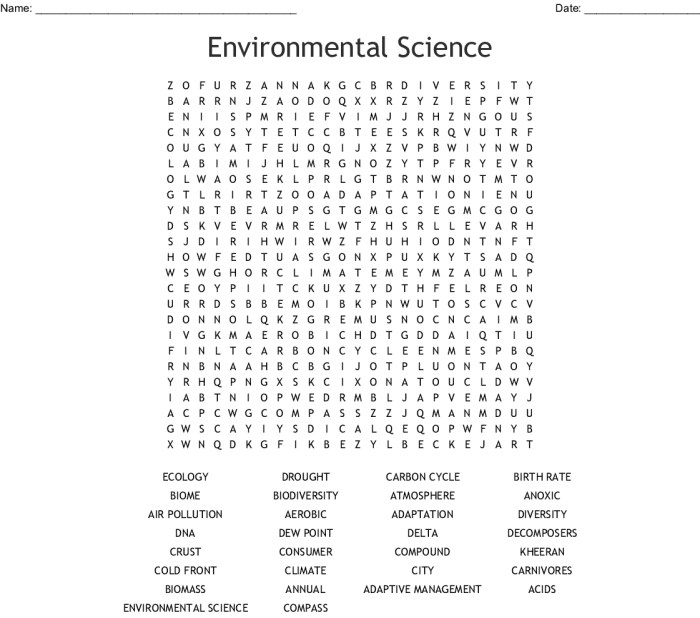
Environmental Science Concepts
Environmental science examines the interactions between the natural environment, human activities, and their consequences. It acknowledges the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere.
Human activities significantly impact these systems, potentially leading to environmental issues such as climate change, air and water pollution, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. Understanding these impacts and developing sustainable solutions is crucial for preserving the health of our planet and its inhabitants.
Interconnectedness of Earth’s Systems
Earth’s systems are closely intertwined and influence each other. For example, the atmosphere regulates the Earth’s temperature, while the hydrosphere provides water for all living organisms. The geosphere shapes the Earth’s surface and provides resources, while the biosphere supports life and maintains ecological balance.
- The atmosphere absorbs and releases heat, regulating the Earth’s temperature and climate.
- The hydrosphere stores and distributes water, supporting life and shaping the Earth’s surface.
- The geosphere provides minerals, rocks, and fossil fuels, while shaping the Earth’s topography.
- The biosphere encompasses all living organisms, interacting with each other and the other Earth systems.
Climate Change
Climate change refers to the long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place. It is primarily driven by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping heat and causing global warming.
Causes of Climate Change
- Fossil Fuel Combustion:Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
- Deforestation:Cutting down forests reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb CO2, leading to higher atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Industrial Processes:Certain industrial activities, such as cement production, release greenhouse gases like nitrous oxide (N2O) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
- Agriculture:Livestock farming and rice cultivation contribute to methane (CH4) emissions, while nitrogen-based fertilizers release nitrous oxide.
Effects of Climate Change
Climate change has widespread effects on the Earth’s ecosystems and human populations:
- Rising Sea Levels:As global temperatures increase, glaciers and ice caps melt, causing sea levels to rise, threatening coastal communities and infrastructure.
- Extreme Weather Events:Climate change intensifies the frequency and severity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, heat waves, droughts, and floods.
- Ecosystem Disruption:Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns disrupt ecosystems, affecting plant and animal life, and reducing biodiversity.
- Health Impacts:Climate change can lead to heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems due to air pollution, and the spread of vector-borne diseases.
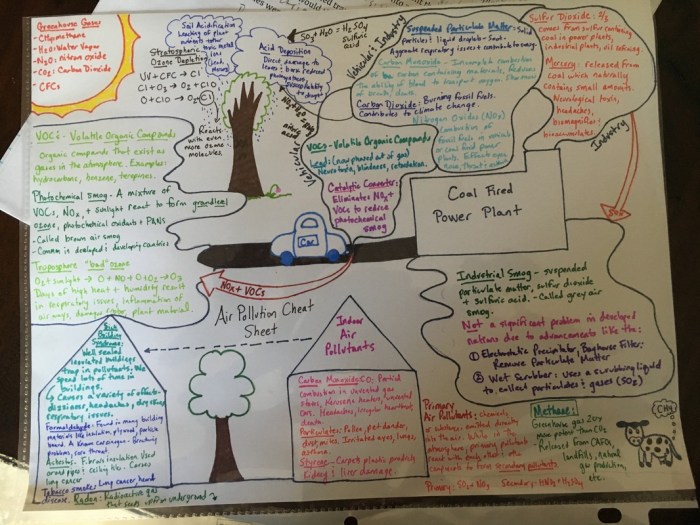
Pollution

Pollution is the contamination of the environment with harmful substances. It can occur in various forms, including air, water, and soil pollution. Pollution can have severe consequences for both the environment and human health.
Air Pollution
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the Earth’s atmosphere. Sources of air pollution include vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and power plants. Air pollution can cause respiratory problems, heart disease, and even cancer.
Water Pollution, Ap environmental science cheat sheet
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Sources of water pollution include sewage discharge, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff. Water pollution can harm aquatic ecosystems and make water unsafe for drinking or swimming.
Soil Pollution
Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil with harmful substances. Sources of soil pollution include industrial waste, pesticides, and fertilizers. Soil pollution can damage plant growth and make soil unsuitable for agricultural purposes.
Importance of Pollution Control and Prevention
Pollution control and prevention measures are crucial to protect the environment and human health. These measures include reducing emissions, treating wastewater, and implementing sustainable agricultural practices. By taking steps to reduce pollution, we can help create a cleaner and healthier environment for ourselves and future generations.
Biodiversity and Conservation

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variation within species. It is essential for the functioning of ecosystems, providing numerous benefits to humans and the environment, including food, medicine, and climate regulation.
However, biodiversity is facing numerous threats, including habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation. These threats have led to a significant decline in biodiversity, with many species becoming endangered or extinct. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect biodiversity and ensure its benefits for future generations.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts involve a range of strategies to protect and restore biodiversity. These efforts can be classified into three main categories:
- Protected areas:Establishing protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, is a common strategy to conserve biodiversity. These areas provide safe havens for species and their habitats, helping to prevent further loss.
- Species conservation:This involves specific measures to protect endangered or threatened species. It may include captive breeding programs, habitat restoration, and the control of invasive species.
- Sustainable use:Promoting sustainable practices in resource use can help to reduce the impact on biodiversity. This includes sustainable agriculture, forestry, and fisheries practices that minimize habitat loss and pollution.
Effectiveness of Conservation Efforts
The effectiveness of conservation efforts varies depending on the specific context and the resources available. However, numerous successful examples demonstrate the positive impact of conservation efforts on biodiversity:
- The Giant Panda:Conservation efforts have helped to stabilize and increase the population of the giant panda, which was once on the brink of extinction due to habitat loss and poaching.
- The American Bison:Conservation efforts, including the establishment of national parks and bison restoration programs, have helped to recover the American bison population from near extinction in the late 19th century.
- The California Condor:Captive breeding and reintroduction programs have helped to increase the population of the California condor, which was once critically endangered due to habitat loss and hunting.
These examples highlight the importance of conservation efforts in protecting biodiversity and ensuring its benefits for future generations.
Sustainable Practices: Ap Environmental Science Cheat Sheet
Sustainable practices are actions and policies that aim to reduce the negative impact of human activities on the environment while ensuring the well-being of current and future generations.
Principles of sustainable development include:
- Intergenerational equity: Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Intra-generational equity: Ensuring a fair and equitable distribution of resources and opportunities within the present generation.
- Precautionary principle: Taking anticipatory action to prevent harm to the environment even when scientific evidence is incomplete.
- Polluter pays principle: Holding those responsible for environmental damage accountable for the costs of remediation and prevention.
Sustainable lifestyles promote practices that minimize environmental footprints, such as reducing energy consumption, conserving water, recycling, and choosing eco-friendly products.
Examples of Sustainable Practices in Various Sectors
Energy:
- Investing in renewable energy sources (e.g., solar, wind, geothermal)
- Improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation
- Promoting the use of electric vehicles
Transportation:
- Developing public transportation systems
- Promoting walking and cycling
- Improving fuel efficiency in vehicles
Agriculture:
- Adopting sustainable farming practices (e.g., crop rotation, no-till farming)
- Reducing the use of pesticides and fertilizers
- Promoting agroforestry and organic farming
Environmental Laws and Regulations
Environmental laws and regulations are crucial for protecting the environment and human health. They establish standards for pollution control, waste management, and conservation efforts.
Key Environmental Laws
- Clean Air Act:Regulates air pollution from stationary and mobile sources.
- Clean Water Act:Protects surface waters from pollution and sets water quality standards.
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA):Regulates hazardous waste disposal and cleanup.
- Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA):Establishes a Superfund program for cleaning up hazardous waste sites.
- Endangered Species Act:Protects threatened and endangered species and their habitats.
Purpose and Enforcement
These laws aim to reduce pollution, protect natural resources, and ensure public health. Enforcement is typically carried out by federal agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and state environmental agencies.
International Agreements
International agreements play a vital role in environmental protection by fostering cooperation and setting global standards. Examples include the Paris Agreement on climate change and the Montreal Protocol on ozone-depleting substances.
Environmental Careers
Environmental science offers a diverse range of career opportunities, catering to individuals with varying interests and expertise. These careers focus on addressing environmental challenges, promoting sustainability, and protecting natural resources.
Education and Skills Required
Pursuing a career in environmental science typically requires a bachelor’s degree in environmental science, ecology, biology, or a related field. Advanced degrees, such as master’s or doctoral degrees, may be necessary for certain specialized roles. Essential skills include:
- Strong scientific foundation in biology, ecology, and chemistry
- Analytical and problem-solving abilities
- Data collection and interpretation skills
- Effective communication and interpersonal skills
- Understanding of environmental regulations and policies
Job Opportunities
Environmental professionals work in various sectors, including:
- Government agencies:Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and state and local environmental departments
- Nonprofit organizations:Environmental Defense Fund, World Wildlife Fund, and Sierra Club
- Private companies:Environmental consulting firms, renewable energy companies, and manufacturing industries with environmental compliance programs
- Education and research institutions:Universities, colleges, and research laboratories
Popular Questions
What is the scope of environmental science?
Environmental science encompasses the study of the interactions between humans and the natural environment, including the impact of human activities on ecosystems, the atmosphere, and the biosphere.
What are the major environmental issues facing our planet today?
Some of the most pressing environmental issues include climate change, pollution, biodiversity loss, deforestation, and water scarcity.
What can individuals do to promote environmental sustainability?
Individuals can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing their carbon footprint, conserving energy and water, recycling and composting, and supporting sustainable businesses and organizations.