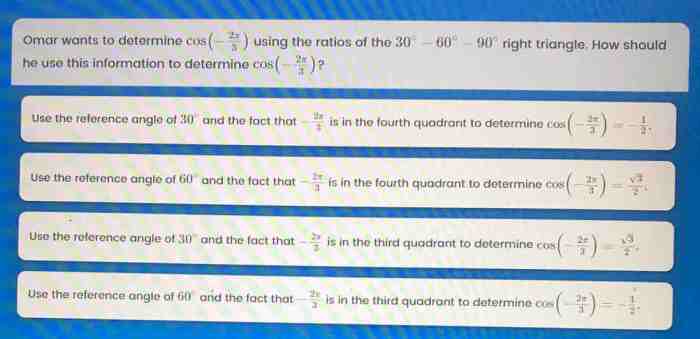
Omar wants to determine cos – Omar’s quest to determine cosine embarks on a journey that unravels the intricacies of trigonometry, revealing its practical applications in our world. From the unit circle to advanced calculus, cosine plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of angles and their relationships.
Delving into the depths of cosine, we will explore its definition, calculation methods, and real-world applications, empowering you with the knowledge to conquer any trigonometric challenge that comes your way.
Understanding the Concept of Cosine
Cosine is a trigonometric function that measures the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle. It is closely related to the unit circle, a circle with a radius of 1 that is used to represent the values of trigonometric functions for all angles.
The trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine, and tangent are defined as follows:
- Sine: the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse
- Cosine: the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse
- Tangent: the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side
Cosine is used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
- Navigation: Cosine is used to calculate the angle between a ship’s course and its destination.
- Engineering: Cosine is used to calculate the forces acting on a structure.
- Astronomy: Cosine is used to calculate the positions of stars and planets.
Determining Cosine Using the Unit Circle

The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1, centered at the origin of the coordinate plane. It is a useful tool for calculating trigonometric ratios, including cosine.
Determining Cosine Using the Unit Circle
To determine the cosine of an angle using the unit circle, follow these steps:
- Draw the unit circle in the coordinate plane.
- Draw the terminal side of the angle on the unit circle.
- Identify the coordinates of the point where the terminal side intersects the unit circle.
- The cosine of the angle is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
For example, to find the cosine of a 30-degree angle, draw the unit circle and draw the terminal side of the angle. The terminal side intersects the unit circle at the point (√3/2, 1/2). Therefore, the cosine of a 30-degree angle is √3/2.
Calculating Cosine Using Trigonometric Functions: Omar Wants To Determine Cos

The cosine function, denoted as cos θ, is a trigonometric function that measures the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle. It is commonly used in trigonometry and geometry to calculate the angles and lengths of triangles.
Calculating Cosine Using a Calculator or Tables
Cosine can be calculated using a calculator or trigonometric tables. Most scientific calculators have a built-in cosine function. To calculate cosine using a calculator, enter the angle in degrees or radians and press the “cos” button. Trigonometric tables provide cosine values for common angles.
Domain and Range of Cosine
The domain of the cosine function is the set of all real numbers. The range of the cosine function is the interval [-1, 1]. This means that cosine can take on any value between -1 and 1, inclusive.
Table of Cosine Values for Common Angles
| Angle (degrees) | Angle (radians) | Cosine |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 30 | π/6 | √3/2 |
| 45 | π/4 | √2/2 |
| 60 | π/3 | 1/2 |
| 90 | π/2 | 0 |
Applications of Cosine in Trigonometry

Cosine is a trigonometric function that finds applications in various areas of trigonometry. It plays a crucial role in solving right triangles and is widely used in fields such as navigation, engineering, and physics.
Solving Right Triangles
In a right triangle, cosine is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. This relationship allows us to find the missing side or angle in a right triangle.
Law of Cosines
The law of cosines is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem for oblique triangles (triangles with no right angles). It states that in a triangle with sides a, b, and c, and an angle C opposite side c, the following equation holds:“`c² = a² + b²
2ab cos(C)
“`The law of cosines is useful for solving oblique triangles when we know two sides and the included angle or two angles and the included side.
Real-World Applications
Cosine has numerous real-world applications, including:
-
-*Navigation
Determining the direction and distance traveled by a ship or aircraft.
-*Engineering
Calculating forces, moments, and stresses in structures.
-*Physics
Omar’s determined to figure out cos, but he’s struggling. I recommend checking out the Lord of the Flies worksheet for some helpful tips. Omar’s got this! He’ll be a cos-determining pro in no time.
Describing the motion of objects in projectile motion and circular motion.
Common Cosine Identities, Omar wants to determine cos
There are several common cosine identities that are useful for solving trigonometric equations and simplifying expressions:
- *cos(π
- θ) =
- cos(θ)
- *cos(π + θ) =
- cos(θ)
- *cos(2θ) = cos²(θ)
- sin²(θ)
- *cos(θ/2) = ±√((1 + cos(θ))/2)
Advanced Applications of Cosine
Cosine finds extensive use in advanced fields such as calculus, physics, and engineering. Its periodic nature makes it a powerful tool for modeling various phenomena.
Calculus
Cosine is a key function in calculus, particularly in the study of derivatives and integrals. The derivative of cosine is negative sine, while its integral is sine. These properties are essential for solving differential equations and finding the area under curves.
Physics
In physics, cosine is used to describe the motion of objects in circular or oscillatory motion. For example, it is used in the equation for simple harmonic motion, which describes the movement of objects like pendulums and springs.
Engineering
Cosine is widely used in engineering, especially in structural analysis and vibration studies. It is used to calculate the forces and stresses on structures, such as bridges and buildings, and to analyze the dynamic behavior of systems.
Modeling Periodic Functions
Cosine is a fundamental function for modeling periodic phenomena. Periodic functions repeat themselves at regular intervals, and cosine’s wave-like shape makes it ideal for representing such behavior. It is used in fields such as signal processing, acoustics, and astronomy to model waveforms and analyze periodic data.
Real-World Applications
- In astronomy, cosine is used to calculate the positions of stars and planets in the sky.
- In acoustics, it is used to design concert halls and other spaces for optimal sound quality.
- In signal processing, it is used to filter out noise and extract useful information from signals.
- In computer graphics, it is used to create realistic lighting and shading effects.
Table of Advanced Cosine Applications
| Field | Application ||—|—|| Calculus | Derivatives, integrals || Physics | Simple harmonic motion, circular motion || Engineering | Structural analysis, vibration studies || Modeling Periodic Functions | Signal processing, acoustics, astronomy || Real-World Applications | Astronomy, acoustics, signal processing, computer graphics |
Answers to Common Questions
What is the cosine function?
The cosine function is a trigonometric function that calculates the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle for a given angle.
How do I calculate cosine using the unit circle?
To calculate cosine using the unit circle, locate the point on the circle that corresponds to the given angle and determine its x-coordinate. The x-coordinate represents the cosine of the angle.
What are some real-world applications of cosine?
Cosine has numerous applications, including solving right triangles, calculating distances in navigation, modeling periodic functions, and analyzing sound waves.